
In the header record, the information is encoded in the ASCII standards to ensure flexibility across distinct architectures using distinct byte orderings. The file header record includes the metadata of a file. Two tar formats are written in POSIX: pax and ustar. There are many tar file formats available, including current and historical ones. Since Microsoft 10 April 2018 Update, BSD-tar has been contained in Microsoft Windows, and there are two or more third-party tools to read and write these patterns on Windows. Unix-like operating systems generally contain tools for supporting tar files and utilities used for compressing them, like bzip2 and gzip. To store the data, the file structure was standardized in POSIX.1-1988 and later POSIX.1-2001 and became a pattern supported by almost all modern file archiving systems. In favor of pax, POSIX abandoned tar, tar yet sees widespread use.įirst, it was announced in Version 7 Unix in January 1979, substituting the tp program.
#Untar command linux tar.gz archive#
The archive data groups made by tar include many file system parameters like directory organization, file access permission, ownership, timestamps, and name. The title is acquired from "tape archive" because it was actually developed to specify data on sequential I/O devices using none of their file systems. Often, it is known as tarball for backup and distribution purposes. Tar is a utility of computer software to collect several files into a single archive file in computing. We can use this command for creating uncompressed and compressed archive files and modify and maintain them as well. In Linux, it is one of the essential commands which facilitate archiving functionality.
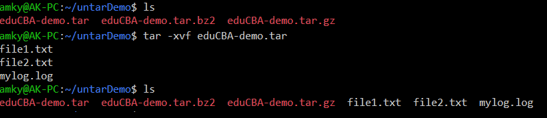
This command is used for creating Archive and extracting the archive files. The tar command is short for tape archive in Linux. Next → ← prev Tar command in Linux/Unix with Examples


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
